Setup
ssh into one of the Kali VMs that has been brought up on Compute Engine in the bsidespdx25 project.
In your home directory, clone the repository the exercises reside in.
git clone https://github.com/wu4f/cs475-src
Change into the exercise directory.
cd cs475-src/04_MCP/01_sqlite
There are two main ways of running an MCP server. One way is to run the MCP server locally and communicate with it over standard input/output (STDIO) while another is to run the MCP server remotely and communicate with it over HTTP. For this exercise, we'll first utilize the local method.
MCP server
The code below implements the SQLite server. The description of the tool is provided within the comments of the tool declaration and is used to instruct the LLM on its use. An LLM agent is better equipped to call MCP tools if these descriptions are detailed, specific, and accurate. It utilizes the FastMCP package to create the server and instantiates one tool within it called query(). The tool handles queries to a local SQLite database by taking a query string and executing it against the database, returning the results. By taking a raw query string, the tool is vulnerable to prompt injection and SQL injection attacks.
vulnerable_sqlite_mcp_server.py
from fastmcp import FastMCP
import sqlite3
import sys
mcp = FastMCP("sqlite")
con = sqlite3.connect('db_data/metactf_users.db')
@mcp.tool()
async def query(query: str) -> list:
"""Query a specified Sqlite3 database. Takes a query string as an input parameter and returns the result of the query."""
cur = con.cursor()
res = cur.execute(query)
con.commit()
return res.fetchall()
if __name__ == "__main__":
if sys.argv[1] == 'stdio':
mcp.run(transport="stdio")
else:
mcp.run(transport="http", host="0.0.0.0", port=8080)To leverage this server, we'll need to instantiate a client agent.
MCP client
FastAgent is an implementation of agents designed specifically for MCP tool calls and their results. The agent is simple to set up and can easily leverage the MCP server. To begin with, FastAgent needs to be configured with the name and functionality of the MCP servers it is allowed to access. The configuration for utilizing the vulnerable SQLite STDIO MCP server is shown below. A FastAgent client will automatically load this configuration to initialize its tools.
fastagent.config.yaml
mcp:
servers:
vulnerable_sqlite_stdio:
command: "python"
args: ["vulnerable_sqlite_mcp_server.py","stdio"]A simple FastAgent program can then be written to utilize this MCP server to answer queries.
fastagent_mcp_client.py
import asyncio
from fast_agent.core.fastagent import FastAgent
# Create the application
fast = FastAgent("SQLite Agent")
@fast.agent(
instruction=f"You are a Sqlite3 database look up tool. Perform queries on the database given the user's input. Utilize the user input verbatim when sending the query to the database and print the query that was sent to the database",
model="gpt-4.1",
servers=["vulnerable_sqlite_stdio"],
use_history=True,
)
async def main():
async with fast.run() as agent:
await agent.interactive()
if __name__ == "__main__":
asyncio.run(main())As shown in the agent, the model utilized is hard-coded. You may select alternate models from the list provided by FastAgent here.
To run the agent and MCP server, create a virtual environment and install the packages required using the uv package manager.
uv init uv add -r requirements.txt
Then, run the agent and interact with the interactive interface implemented by the FastAgent package.
uv run fastagent_mcp_client.py
Attempt to interact with the database using the agent.
- List all tables
- How many users are in this database?
- List all usernames that begin with the letter 'a'
- Find the admin user in the database and output the password hash.
- What password hash algorithm and number of iterations are being used to store hashes?
- Find the user table and identify the columns that contain a username and password hash. Then, find the password hash for the admin user. Then, find the type of password hash it is. Finally, write a hashcat command to perform a dictionary search on the password.
It is quite dangerous to expose an MCP server like this without proper access control. Using the agent, show whether the server is vulnerable to attack using the queries below.
- List the passhash of
foo or 1=1-- - Drop the users table
Type /exit to exit out of the agent.
If the agent is able to delete the table, restore it from the command line via:
git checkout db_data/metactf_users.db
The prior MCP server was insecurely designed, allowing an agent excessive access to the underlying database. Secure MCP server design must address adversarial use of an agent. In this exercise, we'll limit the scope of the MCP server's access in order to prevent the prior compromises of the database.
MCP server
Rather than provide raw query access to the database, the server code below restricts access by implementing two very specific, read-only access mechanisms to the database. It also utilizes a parameterized query to protect against SQL injection attacks via the username parameter.
secure_sqlite_mcp_server.py
from fastmcp import FastMCP
import sqlite3
import sys
mcp = FastMCP("sqlite")
con = sqlite3.connect('db_data/metactf_users.db')
@mcp.tool()
async def fetch_users() -> list:
"""Fetch the users in the database. Takes no arguments and returns a list of users."""
cur = con.cursor()
res = cur.execute('SELECT username from USERS')
return res.fetchall()
@mcp.tool()
async def fetch_users_pass(username: str) -> str:
"""Useful when you want to fetch a password hash for a particular user. Takes a username as a string argument. Returns a JSON string"""
cur = con.cursor()
res = cur.execute(f"SELECT passhash FROM users WHERE username = ?;", (username,)
return res.fetchone()[0]
if __name__ == "__main__":
if sys.argv[1] == 'stdio':
mcp.run(transport="stdio")
else:
mcp.run(transport="http", host="0.0.0.0", port=8080)To leverage this server, we'll need to instantiate a client agent.
MCP client
FastAgent is an implementation of agents designed specifically for MCP tool calls and their results. The agent is simple to set up and can easily leverage the MCP server. To begin with, FastAgent needs to be configured with the name and functionality of the MCP servers it is allowed to access. The configuration for utilizing the vulnerable SQLite STDIO MCP server is shown below. A FastAgent client will automatically load this configuration to initialize its tools.
fastagent.config.yaml
mcp:
servers:
secure_sqlite_stdio:
command: "python"
args: ["secure_sqlite_mcp_server.py","stdio"]A simple FastAgent program can then be written to utilize this MCP server to answer queries.
fastagent_mcp_client.py
import asyncio
from fast_agent.core.fastagent import FastAgent
...
@fast.agent(
...,
servers=["secure_sqlite_stdio"],
...,
)After changing the agent and its configuration to utilize the secure version of the MCP server, run the agent and interact with the interactive interface implemented by the FastAgent package.
uv run fastagent_mcp_client.py
Attempt to interact with the database using the agent as before
- List all tables
- How many users are in this database?
- List all usernames that begin with the letter 'a'
- Find the admin user in the database and output the password hash.
- What password hash algorithm and number of iterations are being used to store hashes?
- Find the user table and identify the columns that contain a username and password hash. Then, find the password hash for the admin user. Then, find the type of password hash it is. Finally, write a hashcat command to perform a dictionary search on the password.
With a more secure implementation, show whether the server is vulnerable to attack using the queries below.
- List the passhash of
foo or 1=1-- - Drop the users table
Type /exit to exit out of the agent.
- Is there a prompt you can inject to drop the users table?
One can also run an MCP server remotely over the network, thus allowing MCP clients to invoke the tools that the server implements over the network using HTTP. In this exercise, an instance of the secure SQLite MCP server has been deployed in a serverless manner in a container running on Google's Cloud Run. The Dockerfile for the container that has been deployed is shown below.
Dockerfile
FROM python:3.10
WORKDIR /app
COPY requirements.txt .
RUN pip install --no-cache-dir -r requirements.txt
RUN mkdir -p db_data
COPY secure_sqlite_mcp_server.py .
COPY ./db_data/metactf_users.db ./db_data/metactf_users.db
EXPOSE 8080
CMD ["python", "secure_sqlite_mcp_server.py", "http"]MCP server
Visit Cloud Run and click on the container deployment to obtain its URL.
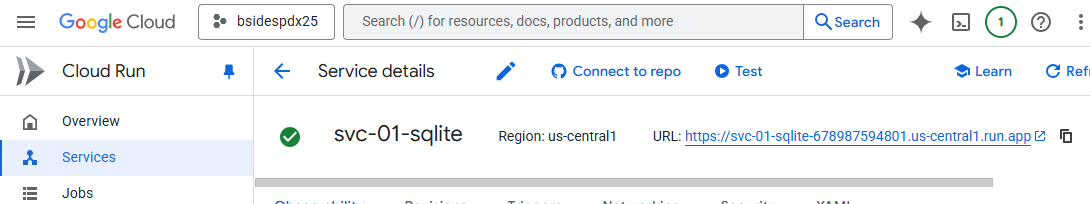
MCP client
To leverage this server, we'll need to configure the client agent with the URL. Edit the configuration file for the agent, and fill in the serverless endpoint URL. Append the /mcp/ route to the URL as that is the default endpoint used for FastMCP.
fastagent.config.yaml
mcp:
servers:
secure_sqlite_sse:
transport: http
url: "https://....a.run.app/mcp/"Then, reconfigure the FastAgent program to utilize this newly configured server to answer queries.
fastagent_mcp_client.py
import asyncio
from fast_agent.core.fastagent import FastAgent
...
@fast.agent(
...,
servers=["secure_sqlite_sse"],
...,
)After changing the agent and its configuration to utilize the Cloud Run version of the MCP server, run the agent and interact with the interactive interface implemented by the FastAgent package.
uv run fastagent_mcp_client.py
Attempt to interact with the database using the agent as before
- List all tables
- How many users are in this database?
- List all usernames that begin with the letter 'a'
- Find the admin user in the database and output the password hash.
- What password hash algorithm and number of iterations are being used to store hashes?
- Find the user table and identify the columns that contain a username and password hash. Then, find the password hash for the admin user. Then, find the type of password hash it is. Finally, write a hashcat command to perform a dictionary search on the password.
With a more secure implementation, show whether the server is vulnerable to attack using the queries below.
- List the passhash of
foo or 1=1-- - Drop the users table
Type /exit to exit out of the agent.
- Is there a prompt you can inject to drop the users table?